Gout in Wilmington - Rheumatology Center of Delaware
We offer the latest quality, state of the art medical care yet in a personable setting. We aim to meld the cutting edge specialist medical care that our clients expect in a comfortable family-oriented atmosphere.
Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Gout is an inflammatory arthritis causing pain, swelling, and redness in joints due to uric acid buildup. With proper management, symptoms can be reduced and attacks prevented. This article covers the causes, symptoms, and treatment of gout.
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Purine byproduct is a waste product that the body produces when breaking down purines, which are found in certain foods and drinks. When Serum urate levels become too high, it can form sharp crystals in the joints, leading to painful gout attacks.
Causes of Gout
Gout is caused by high Serum urate levels in the blood (hyperuricemia), which occurs when the body produces too much or the kidneys can’t excrete it properly. Factors like diet, genetics, and other health conditions can contribute to this.
How Uric Acid Levels Affect Gout
High uric acid levels are the key factor in the development of gout. When Serum urate levels exceed the kidneys’ ability to filter it, the excess acid forms uric acid crystals. These crystals then deposit in the joints, triggering painful gout attacks. Over time, repeated Gout episodes can damage the joints.
SIGNS/SYMPTOMS
Intense Joint Pain:
Gout commonly causes sudden, severe pain, often in the big toe, which can make even light touch or pressure unbearable.Swelling and Redness:
The affected joint may become swollen, red, and warm to the touch, signaling inflammation due to uric acid buildup.Sudden Onset of Pain:
Gout attacks typically begin suddenly, often at night, and the pain can peak within hours, lasting from a few days to weeks if untreated.Restricted Range of Motion:
The joint affected by gout can become so painful that it’s difficult to move or bend, limiting daily activities.Lingering Discomfort After Attack:
After the severe pain subsides, a lingering discomfort or sensitivity may remain in the affected joint for days or weeks.Tophi (Uratic Crystals Deposits):
Over time, uric acid crystals may form lumps under the skin, known as tophi, which can appear on joints, tendons, or ears.Fever:
A mild fever sometimes accompanies a gout attack, as the body reacts to the inflammation caused by uric acid buildup.
LIVING WITH GOUT
Managing Flare-Ups:
Gout flare-ups often require careful management, including monitoring diet and taking medications to prevent painful episodes.Watching What You Eat:
Lifestyle changes, such as limiting red meat, alcohol, and foods high in purines, are crucial to reducing the frequency of gout attacks.Medication Routine:
Daily medications help lower uric acid levels, but it’s important to follow a doctor’s advice to avoid long-term joint damage.Chronic Joint Pain:
Even between flare-ups, lingering discomfort in the joints can remain, requiring a balance between activity and rest for pain management.Dietary Adjustments:
Avoiding shellfish, sugary drinks, and high-fat dairy can help control gout symptoms and prevent worsening of the condition.Staying Active with Caution:
Regular exercise is important, but low-impact activities like swimming or walking are recommended to prevent strain on the joints.Coping with Swelling:
When swelling occurs, elevating and icing affected joints can reduce inflammation and provide relief, helping prevent further pain.
Foods That Can Help Prevent Gout Flares
On the other hand, certain foods can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of Gout episodes. Foods such as cherries, low-fat dairy products, whole grains, and vegetables are beneficial for people with gout. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also essential for managing Serum urate levels.
Treatment for Gout
Managing gout involves lowering Serum urate levels and preventing future gout attacks. Treatment options include medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments.
Preventing Gout Attacks
Preventing gout attacks is crucial for managing the condition. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and avoiding purine-rich foods, can help lower Serum urate levels and reduce the frequency of gout attacks.
Long-Term Management of Gout
Gout is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. With the right treatment plan, people with gout can live a gout-free life and prevent painful flares. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential for managing gout and adjusting treatment as needed.
OUR MEDICAL CLINIC SERVICES IN WILMINGTON, DELAWARE
WILMINGTON SPECIALIZE IN RHEUMATOLOGY AND INFUSION THERAPY
Our Wilmington facility is committed to providing expert care in rheumatology and infusion therapy. Specializing in the treatment of complex autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, we deliver personalized diagnosis and management to meet your unique healthcare needs. Utilizing state-of-the-art medical technology, our infusion therapy services ensure the safe and effective administration of treatments in a comfortable and professional setting. Trust Wilmington’s dedicated team of specialists to deliver compassionate, high-quality care focused on improving your health and overall well-being.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Crohn’s
Osteoarthritis
Psoriasis and
Psoriatic Arthritis
Systemic Lupus
Ulcerative colitis
Joint injections
Connective
tissue disease
Osteoporosis
Temporal arteritis
Vasculitis
Generalized
joint pain
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Gout
Fibromyalgia
Polymyalgia
rheumatica
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Crohn’s
Osteoarthritis
Psoriasis and
Psoriatic Arthritis
Systemic Lupus
Ulcerative colitis
Joint injections
Connective
tissue disease
Osteoporosis
Temporal arteritis
Vasculitis
Generalized
joint pain
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Gout
Fibromyalgia
Polymyalgia
rheumatica
Areas Rheumatology Center of Delaware Cares
Wilmington
Wilmington facility is committed to providing expert care in...
Dover
Dover Urgent Care offers prompt medical attention for...
Milford
Milford facility is dedicated to providing specialized care in...
Areas Rheumatology Center of Delaware Cares
Wilmington
Wilmington facility is committed to providing expert care in...
Dover
Dover Urgent Care offers prompt medical attention for...
Wilmington
Milford facility is dedicated to providing specialized care in...
RHEUMATOLOGY CENTER OF DELAWARE FAQs ABOUT GOUT
What is gout?
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can lead to the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints, causing pain and inflammation.
What are the main symptoms of gout?
Common symptoms include intense joint pain (often in the big toe), swelling, redness, warmth, and limited range of motion, particularly during flare-ups.
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by elevated uric acid levels in the body, which can occur due to factors like diet (high purine foods), obesity, genetics, and certain medical conditions.
How is gout diagnosed?
Gout is diagnosed through a physical examination, blood tests to measure uric acid levels, and sometimes a joint aspiration to check for uric acid crystals.
How is gout treated?
Treatment typically involves anti-inflammatory medications (like NSAIDs or colchicine), uric acid-lowering medications (like allopurinol), and lifestyle changes such as diet adjustments and weight management.
Is gout hereditary?
Yes, gout can run in families, and genetics can play a role in the body’s ability to process uric acid, making some individuals more prone to developing it.

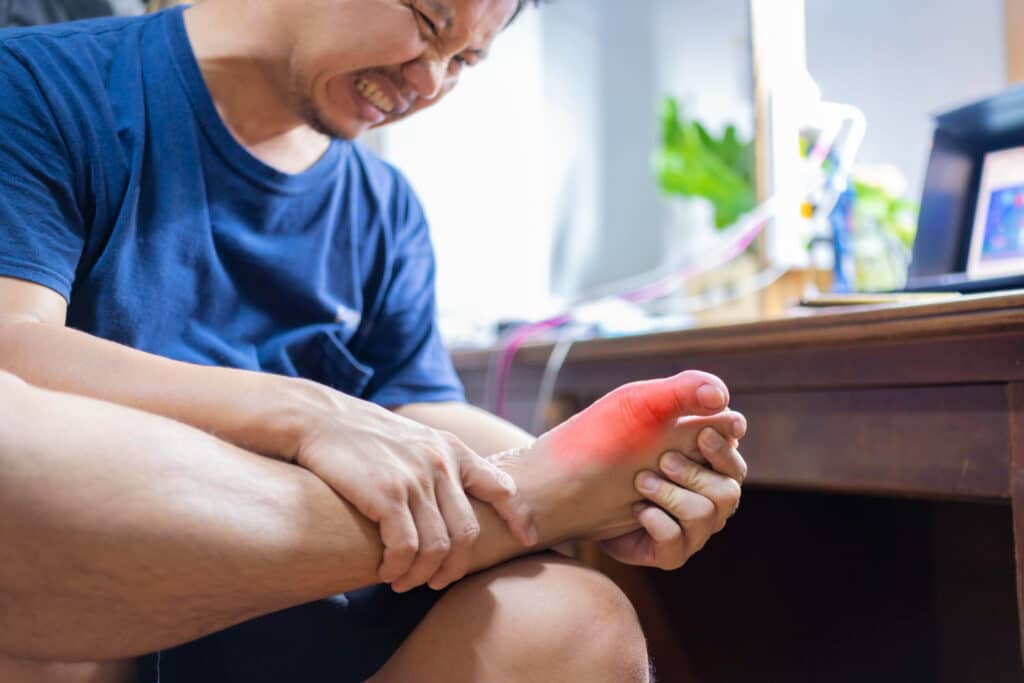
Managing Gout Flare-Ups
When a gout flare-up occurs, it is important to take immediate action to reduce pain and inflammation. Medications, rest, and ice packs can help manage symptoms during a flare-up. Prompt treatment can prevent the flare from becoming more severe.
Contact Information
- 302-994-2345
- 4512 Kirkwood Hwy Wilmington, DE 19808, USA
Enjoy the Outdoors at Rocky Run YMCA and Park
Visit Rocky Run YMCA and Park, a local gem offering hiking trails, a playground, and recreational facilities perfect for family outings and outdoor activities. Whether you’re hiking through scenic trails or enjoying the park’s amenities, it’s an ideal spot for all ages to stay active and connect with nature.
At the Rheumatology Center in Wilmington, Delaware, specialized care is available to manage gout and prevent flare-ups. Personalized treatment plans focus on reducing uric acid levels, managing pain, and preventing future attacks. With advanced treatment options and a focus on long-term relief, the goal is to help regain control of health and enjoy a pain-free lifestyle. Don’t let gout affect your quality of life schedule a consultation today and take the first step toward effective treatment and better health.







